Iboga is a sacred plant native to the tropical regions of Central Africa, especially in countries such as Gabon, Cameroon, and the Republic of the Congo. Since ancient times, it has played a crucial role in various indigenous communities’ spiritual and healing ceremonies, especially within the Bwiti religion. Iboga is distinguished from other sacred plants’ active ingredient, ibogaine, an alkaloid with psychoactive and therapeutic properties that has captured the attention of modern science.
Over the past few decades, ibogaine has been the subject of numerous studies for its ability to interrupt substance addiction and for its potential to treat various mental conditions. However, its use remains controversial due to the associated risks and lack of regulation in many countries. In this article, we will explore in depth what Iboga is, how ibogaine is synthesized, its effects on the body, and the possible medicinal applications that could revolutionize the treatment of addictions and other diseases.
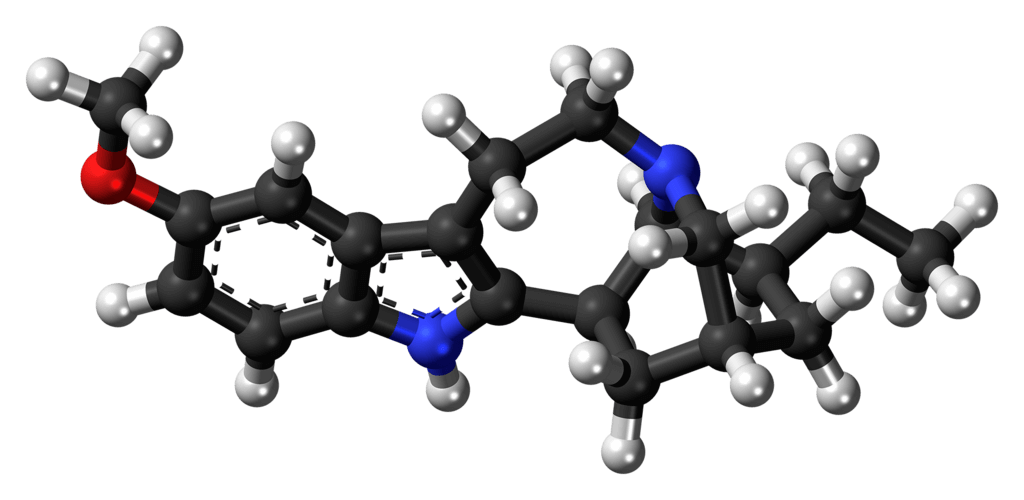
What is Iboga?
Iboga, scientifically known as Tabernanthe iboga, is an evergreen shrub that can reach up to 2 meters in height, with oval leaves and small white or yellow flowers. It is native to the rainforests of Central and West Africa and has been used for centuries by local tribes in religious and medicinal practices. The most valuable part of the plant is its root, which contains several alkaloids, with ibogaine being the most potent and studied.
In the Bwiti religion, Iboga root is consumed in initiation and healing ceremonies, where it is believed to facilitate contact with ancestral spirits and provide deep spiritual insight. The effects of Iboga in these ceremonies can last for several hours or even days, during which participants experience intense visions and altered states of consciousness. The plant is considered a sacred sacrament, and its use is deeply rooted in the culture and spirituality of these communities.
Aside from its ceremonial use, Iboga has also been used in traditional medicine to treat various conditions, from fever and pain to infectious diseases. However, its true value has only recently been recognized in the realm of modern medicine, where ibogaine has been identified as a potentially revolutionary treatment for substance addiction, leading to renewed interest in the plant and its properties.

Ibogaine synthesis
Ibogaine (C20H26N2O), the main active alkaloid of Iboga, is a molecule of complex structure found mainly in the root bark of the plant. Its natural extraction involves a process of harvesting the root, followed by isolation and purification of the alkaloids present. However, due to the increasing demand and the need to preserve the plant in its natural habitat, methods have been developed to synthesize ibogaine in a laboratory setting.
The chemical synthesis of ibogaine is a technically challenging process due to its complex indole structure. Synthetic methods typically involve the construction of the indole core, followed by the formation of a series of fused rings that are characteristic of ibogaine. This process not only requires a series of carefully controlled chemical reactions, but also the precise manipulation of reactive intermediates. Although the process is costly and laborious, laboratory synthesis offers a viable alternative to natural extraction, allowing for more sustainable and controlled production of ibogaine.
Ketamine: therapeutic use and main effects
Ketamine, first synthesized in the 1960s, is a versatile drug used in fields such as anesthesia and pain management. In recent years, it has proven effective in treating psychiatric disorders such as resistant depression and PTSD. Although known for its dissociative effects and recreational use, ketamine offers significant benefits in medicine. Today we invite you to explore its production, applications, and main effects.
In addition to chemical synthesis, biotechnological engineering techniques are also being explored, such as genetically modifying microorganisms to produce ibogaine more efficiently. These innovative approaches have the potential to make ibogaine more accessible for research and treatment while reducing the pressure on natural Iboga populations in Africa.

Effects of Ibogaine
Ibogaine is known for its unique and potent psychoactive effects, which set it apart from other psychedelic substances. Upon ingestion, ibogaine induces an altered state of consciousness that can last between 24 and 48 hours, depending on dosage and individual sensitivity. Initial effects often include a phase of deep introspection, characterized by intense visions and vivid internal dialogue. During this phase, many users report experiencing a “life review,” where they relive past events and confront repressed emotions. This process of introspection is often described as therapeutic, allowing people to confront trauma and self-destructive behavior patterns.
In addition to its psychoactive effects, ibogaine has a notable action on the central nervous system, where it acts as a modulator of the neurotransmitter system. In particular, ibogaine can disrupt dependency circuits in the brain, which has led to its use as a powerful tool for treating addiction to drugs such as heroin, cocaine, and alcohol. Studies suggest that ibogaine significantly reduces withdrawal symptoms and compulsive cravings, thus facilitating addiction recovery.
However, the use of ibogaine is not without risks. Ibogaine has been documented to cause serious side effects, including cardiac arrhythmias, which in some cases can be fatal. For this reason, its use should be done under strict medical supervision, in a controlled environment, and with proper monitoring of the patient’s vital signs.

Possible medicinal applications of Iboga
The therapeutic potential of ibogaine has sparked considerable interest in the medical and scientific community, especially in the treatment of addiction. As you have seen, clinical and anecdotal studies have shown that ibogaine can be effective in interrupting dependence on opiates, stimulants, alcohol, and other substances, providing significant relief from withdrawal symptoms and a reduction in cravings. This has led to ibogaine being considered a promising treatment option for addiction, especially in cases where other treatments have failed.
In addition to addiction treatment, other medicinal applications of ibogaine are being investigated. For example, its use in the treatment of depressive and anxiety disorders has been explored, where its ability to induce a state of deep introspection could help patients confront and process underlying emotions. It has also been proposed that ibogaine could have applications in the treatment of neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease, due to its neuroprotective and regenerative effects.

What is Psilocybin and what are its effects?
After decades of neglect, psilocybin is nowadays the subject of dozens of studies and clinical trials all over the world, showing especially promising results in the treatment of conditions like depression or anxiety. In addition to its well-known properties in recreational or spiritual contexts, the news regarding its possible medicinal properties further adds to the interest to this compound.
However, as we have seen in this Blog with many other compounds, it is important to stress that research on ibogaine is still in its early stages, and more evidence is needed to confirm its efficacy and safety in treating these conditions. Currently, the use of ibogaine is limited by legal and ethical issues, as well as by the risks associated with its administration. As research progresses, new therapeutic approaches will likely be developed that can take advantage of the unique properties of ibogaine, opening up new possibilities for the treatment of addictions and other mental and neurological disorders.
As always, we will keep you informed!
Source link
#Iboga #medicinal #treasure #discovered #Alchimia #Grow #Shop